Nvidia and Intel have announced a strategic partnership to jointly develop custom products for data centers and personal computers. This collaboration aims to combine Nvidia's leadership in artificial intelligence and accelerated computing with Intel's central processing unit (CPU) technologies, creating new competitive pressures for Advanced Micro Devices (AMD).
As part of the agreement, Nvidia will make a significant $5 billion investment in Intel stock, acquiring shares at $23.28 each, pending regulatory approval. The announcement prompted a 22.8% rally in Intel's stock price, signaling market optimism about the alliance's potential to reshape the semiconductor industry.
Key Takeaways
- Nvidia and Intel are partnering to develop custom chips for data centers and PCs.
- The collaboration will integrate Nvidia's AI platforms with Intel's x86 CPU technology.
- Nvidia plans to invest $5 billion in Intel stock at $23.28 per share.
- The partnership poses a long-term competitive threat to AMD's market share in both key segments.
Details of the Strategic Alliance
The partnership between Nvidia and Intel is structured to leverage the core strengths of each company across multiple product generations. The collaboration will focus on two primary markets: high-performance data centers and consumer-facing PCs.
Data Center and AI Infrastructure
In the data center segment, Intel will be responsible for designing custom x86 processors specifically for Nvidia's requirements. Nvidia will then integrate these specialized CPUs into its comprehensive AI infrastructure platforms, which it sells directly to enterprise and hyperscale customers.
This move is designed to create highly optimized systems that combine Intel's processing power with Nvidia's dominance in AI accelerators, potentially offering a compelling alternative to AMD's EPYC server processors.
Next-Generation Personal Computers
For the PC market, the companies will work on developing new system-on-chips (SoCs). These integrated chips will feature Intel's CPU architecture alongside Nvidia's RTX GPU chiplets. The resulting products, described as x86 RTX SoCs, are intended to power future PCs that demand advanced computing and graphics performance for gaming, content creation, and AI-driven applications.
The Competitive Landscape
The semiconductor industry has been a three-way competition between Intel, Nvidia, and AMD. While Nvidia dominates the GPU and AI accelerator market, Intel has historically led in CPUs. AMD has successfully competed against both, gaining significant market share in recent years with its Ryzen CPUs and EPYC server chips, as well as its own line of GPUs.
Implications for Advanced Micro Devices (AMD)
The alliance between two of its largest competitors presents a significant long-term challenge for AMD. By working together, Nvidia and Intel could create integrated products that are difficult for AMD to compete against with its standalone offerings.
However, the immediate impact on AMD may be limited. The development of new, co-designed products is a lengthy process, and their market adoption will take even longer. This timeline provides AMD with a window to continue its innovation and solidify its market position with existing and upcoming products.
AMD's Recent Performance
AMD's stock has recently experienced a downturn, falling approximately 15.3% from its 52-week high of $186.65. This decline was partly attributed to softer second-quarter results in its data center business, where AI-related revenue saw a temporary dip.
The company cited two main reasons for the slowdown: U.S. export restrictions that limited sales of its MI308 accelerators to China, and customers pausing orders in anticipation of the new MI350 series launch.
AMD's Current Strengths and Outlook
Despite the new competitive pressure and recent stock performance, AMD maintains a strong position in the market. The company has several growth catalysts expected to drive performance in the near future.
The new MI350 series of AI accelerators is beginning to ramp up production. This launch is widely expected to reaccelerate AI-related revenue within AMD's data center segment. The company is also advancing the development of its next-generation MI400 line, which it reports is already generating strong interest from customers.
"AMD’s EPYC server processors and Ryzen chips are seeing robust adoption, providing multiple growth levers beyond GPUs."
Diversified Revenue and Market Share Gains
AMD's most recent quarterly report demonstrated the resilience of its business model. The company's overall revenue grew 32% year-over-year to $7.7 billion, surpassing analyst expectations. The data center segment alone contributed $3.2 billion, an increase of 14%, even with the temporary weakness in AI sales.
This growth was largely driven by the continued success of its EPYC server processors. According to company reports, the EPYC line has achieved 33 consecutive quarters of market share gains, showing its strong foothold in cloud and enterprise environments.
- Overall Revenue: $7.7 billion (up 32% YoY)
- Data Center Sales: $3.2 billion (up 14% YoY)
- EPYC Market Share: 33 straight quarters of gains
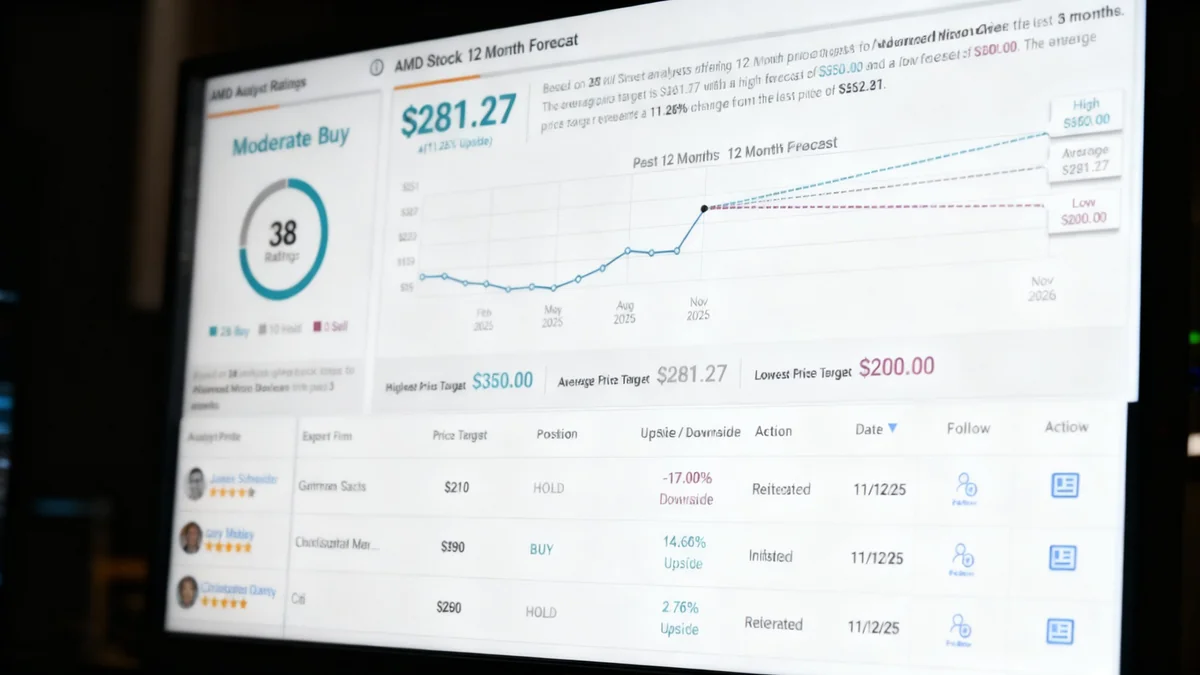
Analyst Perspectives and Investor Opportunity
Analysts currently hold a "Moderate Buy" consensus rating for AMD stock. While the Nvidia-Intel partnership introduces new uncertainty, many believe AMD is well-equipped to handle the increased competition. The company's consistent track record of innovation, strong momentum in the CPU market, and a promising pipeline of AI accelerators are seen as key advantages.
The recent pullback in AMD's share price could be viewed by some investors as a buying opportunity. The company's diversified business, combined with the anticipated ramp-up of its MI350 series and growth in sovereign AI initiatives, positions it for potential future growth.
Ultimately, while the collaboration between Nvidia and Intel creates significant competitive headwinds, AMD's established market presence and ongoing product development suggest it will remain a formidable player in the semiconductor industry.